EXECUTIVE SUMMARY :
At the face of an ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, we address the pressing challenges posed by an transforming realm of cyber threats. With the global cost of cybercrime projected to reach a staggering US$10.5 trillion by 2025, businesses face a compelling reason to bolster their defenses. This report traces the evolution of cyber threats, commencing from simple threats like viruses and phishing attacks to large-scale supply chain breaches. The financial and healthcare sectors particularly emerge as prime targets, given their exposure to vast amounts of sensitive data. The article advocates a comprehensive approach for business leaders, encompassing advanced cybersecurity tools, fortified digital infrastructure, a cyber-aware organizational culture, and strategic leadership for organizational security.
INTRODUCTION
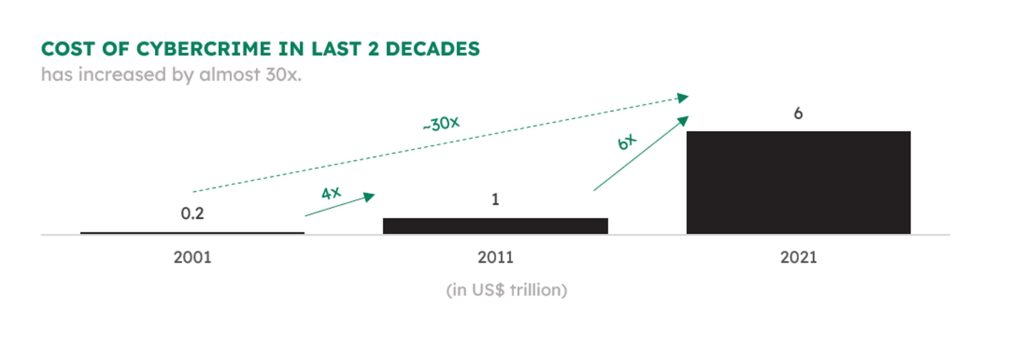
In the ever-evolving landscape of the digital era, the numbers tell a compelling tale—a narrative of both progress and peril. The global cost of cybercrime, a staggering US$8 trillion1 in 2023, looms ominously on the horizon. With 33 billion accounts breached, projections portend an even more formidable figure, poised to reach an unprecedented US$10.5 trillion1 by 2025. To put this in perspective, it emerges as the world’s third-largest economy, eclipsing the combined GDP of Japan and the United Kingdom.
A mere two decades ago, the incipient stirrings of cyber threats manifested in a modest US$0.2 billion2 toll in 2001. The escalation since then is nothing short of seismic a leap to US$1 trillion2 in 2011 and a whopping US$6 trillion2 in 2021. As emerging technologies propel humanity into new frontiers, they concurrently furnish cybercriminals and hackers with potent tools to exploit the expanses of data at their disposal. This duality, the paradox of progress and susceptibility, defines our technological landscape.
THE EVOLUTION OF CYBERCRIME & CYBERSECURITY
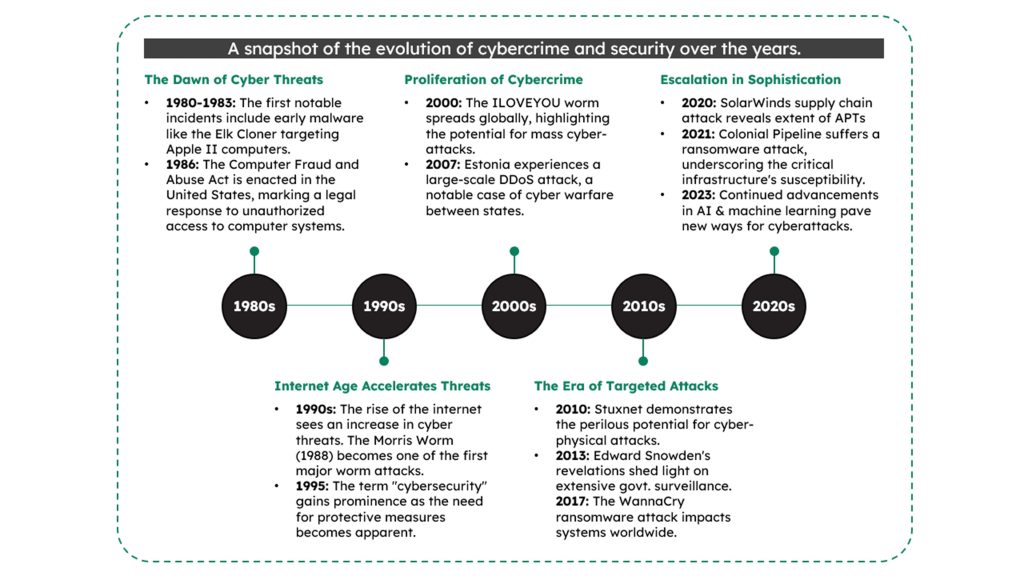
The origins of cybercrime can be traced back to the nascent days of the internet, a time when the digital landscape was still finding its footing. The term “cybersecurity” was coined to describe the measures taken to safeguard computer systems from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
In the 1980s, cyber threats were rudimentary, often involving basic forms of malware and viruses. However, as technology progressed, so did the sophistication of cyber-attacks. The landscape has evolved from simple viruses and worms to complex and targeted forms of cyber threats such as advanced persistent threats (APTs), supply chain disruptions, and ransomware.
The arsenal of cybercriminals has expanded exponentially, encompassing a wide array of tactics, techniques, and procedures designed to exploit vulnerabilities in the interconnected world we inhabit.
IMPACT OF AI IN CYBERSECURITY
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and cutting-edge technologies has ushered in a new era in cybercrime, significantly amplifying both the scale and sophistication of attacks. AI-powered tools enable cybercriminals to automate and optimize their malicious activities, making traditional defense mechanisms less effective. According to recent studies, more than 60% of cybersecurity professionals believe that AI-driven attacks will become more prevalent and harder to detect.
Moreover, the integration of AI into cyber threats has led to the creation of advanced malware and ransomware that can adapt and evolve in real-time, outsmarting conventional security protocols. In 2023 alone, AI-driven cybercrimes are estimated to have caused losses exceeding US$6 billion globally. The concerning aspect is that with AI, one doesn’t need to be an expert to conduct a cybercrime, as these tools provide off-the-shelf capabilities that lower the entry barrier for malicious actors.
SECTOR-SPECIFIC VULNERABILITIES
While cyber threats are pervasive, certain industries are more prone to cyber attacks than others, with the financial and healthcare sectors standing out as prime targets.
Cyber-attacks in the financial sector are often motivated by financial gain. Hackers target banks and financial institutions to steal sensitive information, such as customer data, login credentials, and financial transaction details. This information can then be exploited for identity theft, unauthorized fund transfers, or even sold on the dark web. The consequences extend beyond financial losses, impacting the trust and confidence of customers and investors.
In the healthcare industry, cyberattacks can have life-altering consequences. Ransomware attacks, for instance, can disrupt critical clinical operations, jeopardizing patient care and potentially putting lives at risk. Attackers may encrypt medical records, demanding ransom payments for their release. WannaCry was one such attack targeted at healthcare, impacting stakeholders worldwide.
CASE STUDY: WANNACRY RANSOMWARE 2017
One notable example of a cyber-attack in the healthcare sector is the WannaCry ransomware incident in 2017. The attack targeted the National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom, impacting hospitals and healthcare facilities across the country. WannaCry exploited a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows operating systems, encrypting files and demanding ransom payments in Bitcoin. The ransomware quickly spread through networks, affecting a wide range of organizations globally.
WannaCry infected over 200,000 computers3 in more than 150 countries3, making it one of the largest and most geographically widespread cyberattacks in history. In the United Kingdom, the National Health Service (NHS) bore a substantial brunt of the attack. Around 34% of NHS trusts were directly affected, leading to disruptions in patient care, canceled appointments, and operational challenges. The overall global impact of WannaCry was estimated to be in the billions of dollars.
LANDSCAPE OF CYBERTHREATS
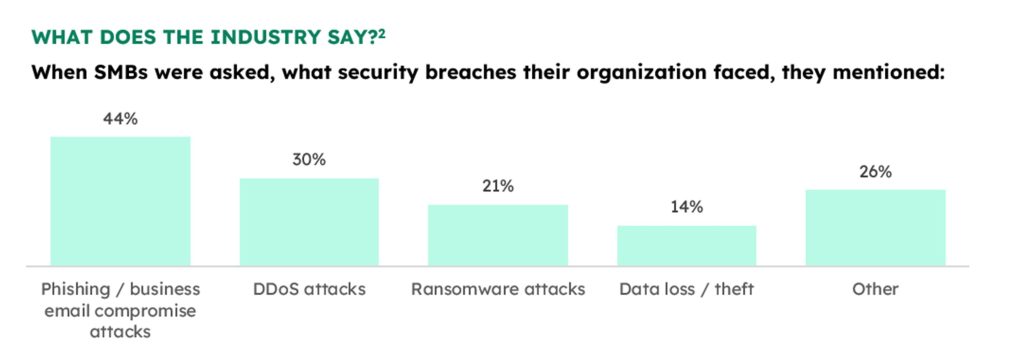
While the cloud of the types of cyberattacks casts a large shadow, the most commonly occurring attacks can be bucketed into one of these categories, arranged in increasing levels of scale and complexity:

Phishing Attacks: Deceptive emails or messages tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information, potentially leading to unauthorized access and data breaches. This can compromise business data integrity and confidentiality.
Ransomware: Malicious software encrypting data and demanding payment for its release, posing a significant threat to business operations and data integrity. Without adequate protection, organizations risk financial losses and operational disruptions.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): Overwhelming a system with traffic, disrupting normal functioning, resulting in downtime and financial losses for businesses. This can lead to a loss in productivity, customer trust and revenue.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM): Intercepting communication between two parties without their knowledge, jeopardizing the confidentiality of sensitive information. Businesses may face breaches of trust and the loss of proprietary information.
SQL Injection: Exploiting vulnerabilities to manipulate a database, potentially gaining unauthorized access, and compromising critical business data. This could result in the compromise of sensitive customer information.
Zero-Day Exploits: Targeting undiscovered software vulnerabilities before they are patched, leaving businesses susceptible to unanticipated breaches and system compromises. This poses a continuous risk to business operations and sensitive data as they do not provide room for security team to analyze the threat until they occurs.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Covert, continuous attacks by sophisticated adversaries over an extended period, posing a sustained risk to business operations and sensitive information. Businesses may face long-term reputational damage.
Insider Threats: Malicious actions or data breaches by individuals within an organization, even caused by negligence, leading to the compromise of confidential data and business secrets.
IoT-Based Attacks: Exploiting vulnerabilities in connected devices to gain unauthorized access, posing a threat to business infrastructure and sensitive data. Businesses risk operational disruptions and compromised data integrity.
Supply Chain Attacks: Compromising systems or software through third-party vendors or service providers, potentially leading to the compromise of business-critical information and operations. This can result in widespread and cascading data breaches.


HOW BUSINESS LEADERS CAN NAVIGATE CYBER CHALLENGES
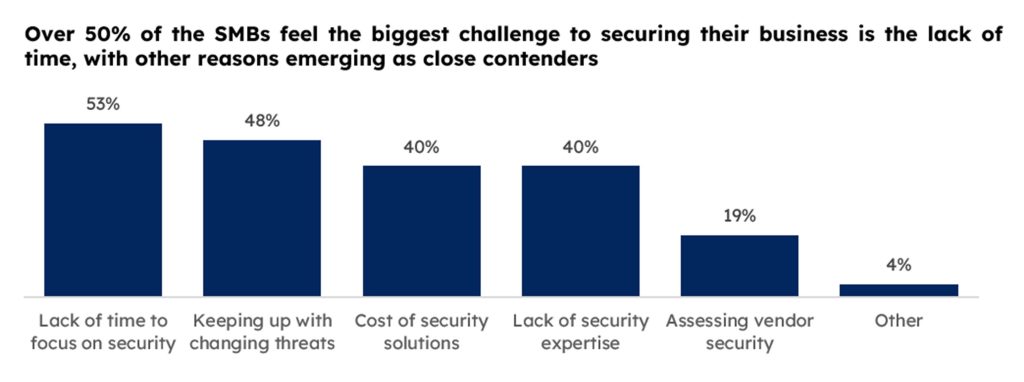
While the threat of cyber attacks looms large, business leaders can play a pivotal role in steering their organizations away from the perilous shores of cybercrime by undertaking certain strategic security measures:
- Investing in cybersecurity tools provides a comprehensive shield against an array of cyber threats. These tools, including antivirus software, firewalls, EDR, EPP, intrusion detection systems, and encryption tools, should be regularly updated and patched to stay ahead of evolving threats.
- Fortifying digital infrastructure involves implementing secure configurations, robust access controls, and multi-factor authentication. Regular assessments and updates to security protocols are crucial to addressing emerging vulnerabilities. Leveraging cloud security solutions can enhance the protection of data and applications.
- Cultivating a cyber-aware culture within the organization is paramount. Regular training sessions that educate employees about common cyber threats, phishing tactics, and security best practices foster a culture of vigilance. Encouraging employees to promptly report suspicious activities strengthens the human firewall.
- For larger organizations, appointing a Chief Security Officer (CSO) is a strategic move. The CSO leads and oversees cybersecurity initiatives, developing and implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, conducting risk assessments, and ensuring regulatory compliance. This dedicated leadership role underscores the strategic importance of cybersecurity.
- Developing a comprehensive incident response plan is essential. This plan outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a cybersecurity incident, ensuring a swift and effective response to mitigate potential damages.
- Implementing robust data encryption protocols safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access. Additionally, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations is essential to avoid legal ramifications and maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders.
- Considering the unpredictable nature of cyber threats, investing in cyber insurance can mitigate financial risks associated with potential breaches. Cyber insurance policies can provide coverage for financial losses, legal expenses, and reputation management.

CONCLUSION
In the expansive landscape of cybersecurity, the challenges may seem daunting and boundless. Yet, within this vast expanse, there exists a realm of proactive defense and strategic resilience mechanisms. Armed with the right mindset & approach and a well-devised plan, individuals and organizations can fortify themselves against the rising tide of cyber threats.
As the frequency and sophistication of cyber attacks escalate, so does the recognition of their significance. The world is now more attuned to the imperative of cybersecurity than ever before. This heightened awareness signifies a positive shift — a collective acknowledgment that safeguarding our digital realms requires not only advanced technology but also a wealth of human capital. It’s a trajectory towards a future where the synergy of technology and human vigilance becomes the cornerstone of our digital defenses. In this era of escalating cyber threats, the emphasis on cybersecurity is not just a necessity; it’s a strategic imperative for a secure and resilient digital future.
References:
1 Cybercrime To Cost The World $10.5 Trillion Annually By 2025 (cybersecurityventures.com)
3 What was the WannaCry ransomware attack? | Cloudflare
For further clarifications or support, please write to ask@paradigmit.com

