In today’s digital landscape, where technology is global and interconnectivity dominates, the security of our systems and data has become more critical than ever before. Unfortunately, the rapid evolution of technology has given rise to a parallel world of vulnerabilities, including one of the most stimulating and dangerous types: zero-day vulnerabilities. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of zero-day vulnerabilities, their implications, and the challenges they pose to cybersecurity professionals.
Understanding Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
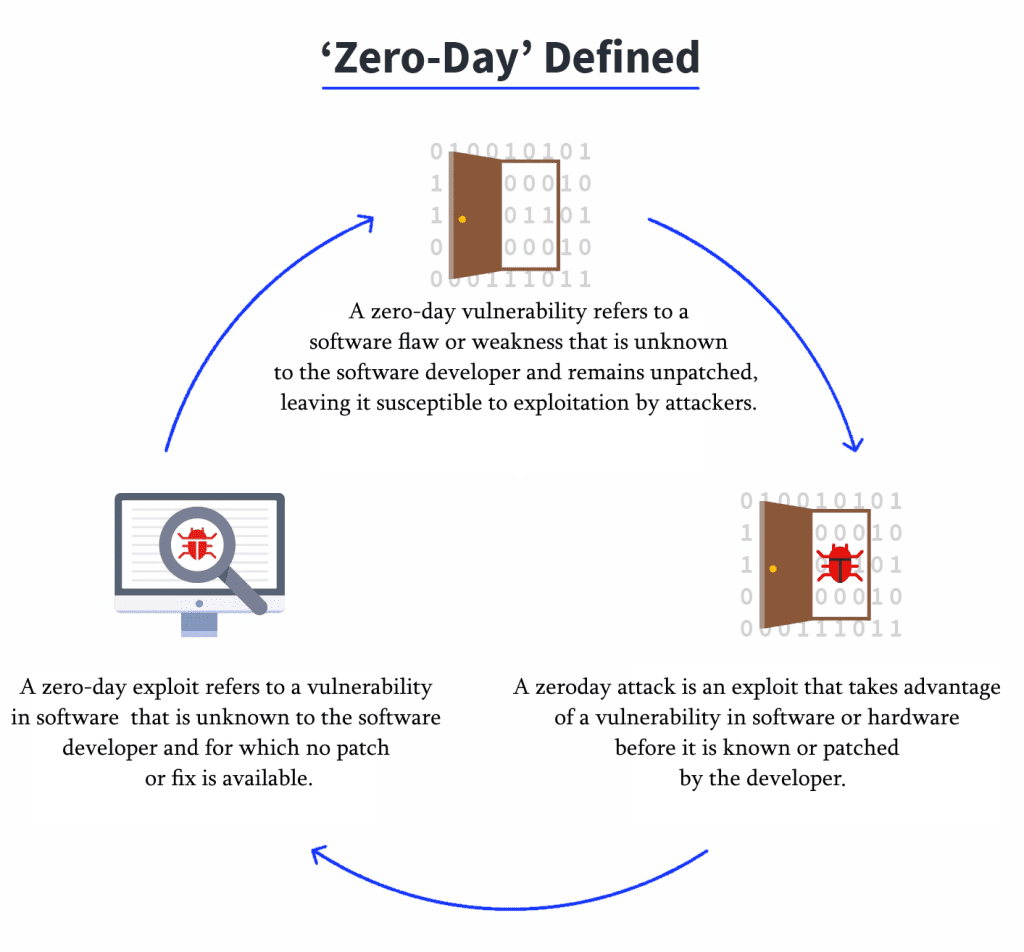
Zero-day vulnerabilities refer to software flaws that are unknown to the developers and remain unpatched, leaving systems exposed to potential exploitation. The term “zero-day” implies that the vulnerability is exploited on the same day it is discovered, leaving no time for the affected party to patch or protect their systems effectively. These vulnerabilities are often discovered by malicious actors or researchers with the intent to exploit or report them, respectively.
The Hidden Threats
Zero-day vulnerabilities pose a significant threat due to their hidden characteristics. Because they remain undisclosed to developers and system owners, there are no established remedies or protective measures to guard against them. Consequently, these vulnerabilities become highly desirable to cybercriminals, who exploit them strategically to execute targeted assaults, acquire unlawful access, and compromise valuable information. The potential outcomes of such attacks are widespread, overarching monetary outcomes, harm to reputation, breaches of national security, and even endangering lives in vital industries such as healthcare or transportation.
Challenges for Cybersecurity Professionals
Zero-day vulnerabilities present significant challenges for cybersecurity professionals. Firstly, identifying these vulnerabilities requires a deep understanding of software and systems architecture, as well as constant vigilance to detect suspicious activities. The complex nature of modern software makes it increasingly difficult to uncover hidden flaws that malicious actors may exploit.
Secondly, once a zero-day vulnerability is discovered, cybersecurity experts face the race against time to develop and deploy effective patches or mitigations before cybercriminals capitalize on the security gap. This requires coordination between vendors, researchers, and affected organizations, often operating under intense pressure to minimize the potential impact.
Dealing with Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Tackling zero-day vulnerabilities requires a comprehensive approach that engages multiple parties. Effectively countering these risks relies on the crucial aspects of cooperation and communication among software vendors, security researchers, and end-users. Encouraging responsible disclosure policies that prompt researchers to directly report vulnerabilities to vendors can speed up the process of fixing them.
Additionally, organizations should take a proactive stance towards cybersecurity by implementing strong defense measures like intrusion detection systems, network segmentation, and ongoing monitoring. Conducting regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify potential vulnerabilities and offer a chance to address them before they become exploitable.
The Exploit Lifecycle and Mitigation Strategies:
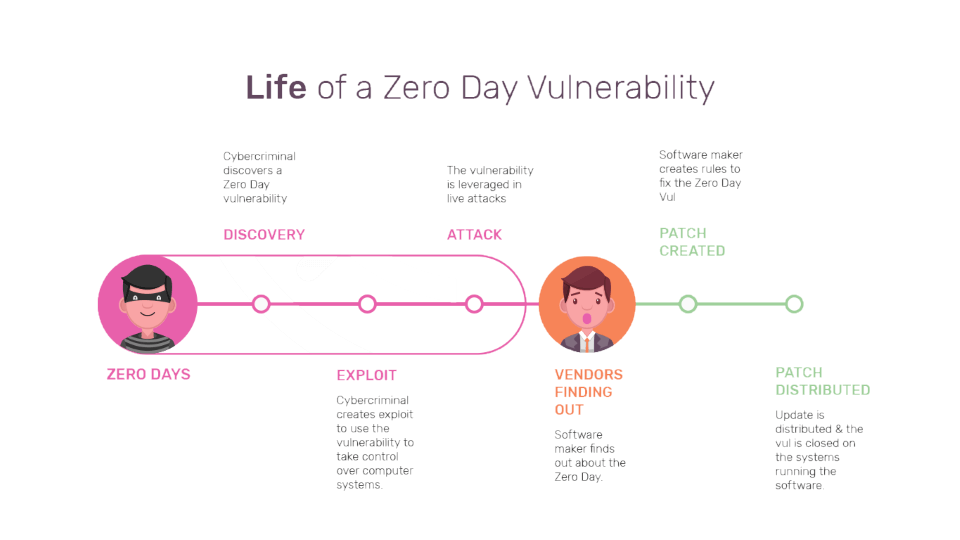
Zero-day vulnerabilities typically follow a lifecycle: discovery, exploitation, exposure, and patching. During the discovery phase, an attacker or a group of researchers identifies the vulnerability, often in secrecy. Once discovered, threat actors develop exploit code to take advantage of the vulnerability’s weaknesses, launching targeted attacks against selected systems. During the exposure phase, the vulnerability becomes public knowledge, exposing systems to potential attacks until a patch or security update is released.
To mitigate the risks associated with zero-day vulnerabilities, organizations, and security researchers employ several strategies:
- The Role of Security Researchers in Vulnerability Research and Disclosure: Security researchers play a crucial role in identifying and reporting previously unknown vulnerabilities to developers. By obeying responsible disclosure practices, researchers provide developers with an opportunity to address these vulnerabilities before they are exploited widely.
- Detecting Intrusions and Analysing Behavior: Organizations can implement advanced intrusion detection systems that monitor network traffic and utilize behavioral analysis to identify suspicious activities and unusual behavior patterns that may indicate the presence of zero-day exploits.
- Leveraging Threat Intelligence and Sharing Information: Organizations can obtain significant benefits by sharing information about zero-day vulnerabilities and associated exploits through trusted channels. This facilitates the enhancement of defensive measures and enables more effective responses to such threats.
- Promoting User Education and Enhancing Security Awareness: By promoting a culture of cybersecurity awareness, organizations can educate users about potential risks and emphasize the importance of regularly updating systems with security patches.
- Strengthening Defences through Application Whitelisting and System Hardening: Implementing techniques like application whitelisting and enforcing precise system hardening measures can minimize the potential attack surface, making it more challenging for malicious actors to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Zero-day vulnerabilities remain a dominant challenge in today’s digital landscape, continuously testing the limits of cybersecurity practices. The ever-evolving threat landscape necessitates increased collaboration, vigilance, and investment in research and development. By fostering a collective effort among software vendors, security researchers, and end-users, we can better safeguard our systems, protect sensitive data, and mitigate the risks posed by these hidden threats. Let us work together to stay one step ahead of the adversaries and ensure a safer digital future.
Citations:
https://teskalabs.com/blog/warning-about-zero-day-vulnerability
https://www.mandiant.com/resources/blog/zero-days-exploited-2022
https://portswigger.net/daily-swig/zero-day
https://www.redlegg.com/blog/security-blog-zero-day-2022-october
For further clarifications or support, please write to contact@paradigmitcyber.com

