a CXO’s handbook for cyber awareness
Executive Summary
Facing a dichotomy between digital innovation and rising cyber threats, healthcare organizations confront escalating attacks, with data breach costs soaring to an industry-high of $7.13 million in 2020. Breaches compromise millions of patient records annually, jeopardizing patient trust and safety. High-profile cases like Monongalia Health System and Anthem Inc. underscore the financial and reputational repercussions of such incidents. Amidst a complex web of digital infrastructure, the healthcare sector must address advanced cyber threats and human vulnerabilities and adhere to stringent regulatory standards like HIPAA. In India, a 45% post-2020 increase in cyber incidents amplifies these challenges, necessitating compliance with national laws such as the IT Act. Healthcare CXOs must foster a proactive cybersecurity strategy, integrating technology, regulatory adherence, and a pervasive security culture to safeguard sensitive data.
Introduction: Unpacking the Alarming Cybersecurity Trends in Healthcare
In an era marked by rapid digitalization, the healthcare industry stands at a critical juncture. It grapples with a paradoxical challenge: leveraging digital innovation for superior patient care while contending with escalating cybersecurity threats. Healthcare organizations are experiencing a surge in cyberattacks, with an estimated average cost of a data breach in the sector reaching $7.13 million in 2020, according to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report. This figure represents a 10% increase over the average cost in the previous year, marking the highest average cost of a breach for any industry for the 10th consecutive year. In terms of patient records, the numbers are equally troubling. The Department of Health and Human Services reports that hundreds of healthcare breaches occur each year, affecting tens of millions of patient records. For instance, in 2020, over 25 million patient records were breached in the United States alone.
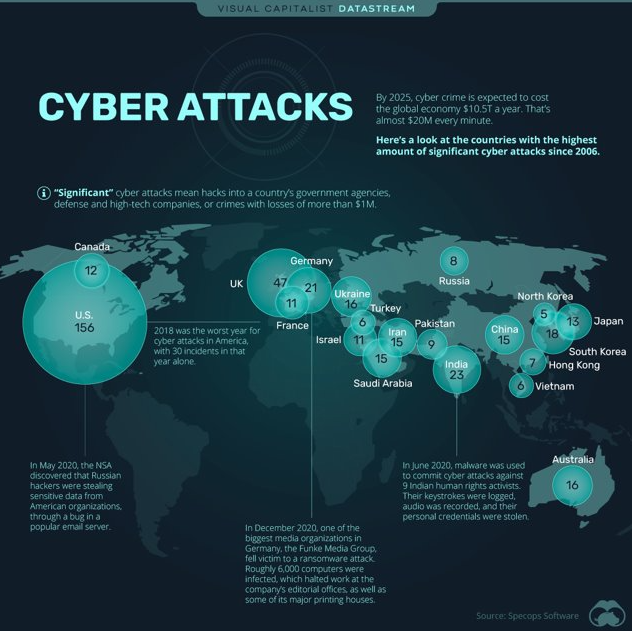
These breaches have a ripple effect, extending far beyond the immediate financial impact. They undermine patient trust, disrupt healthcare delivery, and can lead to critical health data being held ransom or sold on the dark web, potentially resulting in life-threatening situations. As healthcare organizations increasingly adopt digital health records and connected devices, the potential attack surface for cybercriminals widens, necessitating more robust and sophisticated cybersecurity measures. Healthcare entities, repositories of extensive and sensitive patient data, emerge as tantalizing targets for nefarious cyber entities. This data, steeped in both personal and financial details, fetches a premium in the clandestine alleys of the black market. Concurrently, the sector’s increasing entanglement with digital technologies, spanning from the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) to cloud services, amplifies its susceptibility to cyber incursions. The challenge is further exacerbated by legacy security systems that lag behind the evolving sophistication of cyber threats.
In-Depth Case Studies: Cybersecurity Breaches and Lessons Learned

Monongalia Health System Breach (2021):

In July 2021, the Monongalia Health System in West Virginia experienced a sophisticated phishing attack that significantly compromised its cybersecurity. Multiple email accounts were breached, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive patient records. Over 50,000 patient records were exposed, including personal and medical information. The breach had far-reaching implications, resulting in direct financial losses estimated in the hundreds of thousands of dollars. Beyond the immediate financial impact, the incident inflicted considerable reputational damage on the health system. The breach exposed vulnerabilities in the system’s email security protocols and highlighted the critical need for more stringent measures. It also underscored the importance of comprehensive cybersecurity awareness and training among staff. The incident serves as a cautionary tale for healthcare institutions about the potential consequences of phishing attacks and the importance of continuous vigilance and education in cybersecurity practices.
Anthem Inc. Data Breach (2015):

The Anthem Inc. data breach, occurring in February 2015, stands as one of the most significant cybersecurity breaches in the healthcare sector. Hackers successfully infiltrated Anthem’s network, accessing the personal information of nearly 78.8 million individuals. This information included names, dates of birth, social security numbers, healthcare IDs, and even income data. The breach not only affected Anthem’s customers but also impacted employees and individuals affiliated with other health insurance companies that Anthem provided services to.
The scale and severity of the breach led to a landmark settlement of over $115 million, the largest data breach settlement at the time. Furthermore, the incident prompted a nationwide examination of data security practices within the healthcare industry. Anthem’s breach revealed crucial gaps in network security and the need for proactive vulnerability assessments. As a result, it pushed healthcare organizations across the U.S. to reevaluate and strengthen their cybersecurity frameworks. This breach highlighted the need for robust network security measures, ongoing risk assessments, and the implementation of advanced cybersecurity technologies to safeguard sensitive patient data. Anthem’s experience serves as a pivotal learning point for the healthcare industry, emphasizing the importance of robust cybersecurity defenses and the continuous evolution of security strategies to counter emerging cyber threats.
Challenges in the healthcare industry
Navigating Digital Security in Healthcare: Understanding the Complex Network Healthcare’s digital structure is a complex network of connected devices and systems, from electronic health records to critical medical devices. This network is advanced and essential for modern medicine, but also attracts cyber threats. Protecting this digital ecosystem is like securing a city with many entry points, each needing its own protection. It’s a big challenge that requires constant vigilance and a strong defense strategy against the variety of threats that exist online.
The Cyber Threat Landscape: Staying Ahead of Potential Attacks In the world of cybersecurity, attackers are constantly finding new ways to break through defenses. As security technologies improve, so do the tactics of these attackers. They use advanced methods like machine learning and AI to launch precise attacks, often outpacing older security systems. Healthcare organizations need to be proactive, always watching and preparing for these threats. They must quickly respond to attacks and smartly plan ahead to protect sensitive data from relentless cyber threats.
The Human Aspect: Bolstering the First Line of Defense The role of people in cybersecurity is critical, as human actions can either protect or expose healthcare systems to risk. Mistakes like accidental clicks or weak passwords can lead to serious security breaches. The risk from insiders, whether from careless mistakes or harmful intent, remains a serious concern. Strong policies for who can access information and regular training are essential. Building a strong cybersecurity culture within healthcare organizations involves teaching everyone the importance of security and integrating it into their daily work routines.
The Regulatory Odyssey: Charting a Course Through a Sea of Standards
- HIPAA: The beacon of data privacy in the U.S. healthcare domain, HIPAA’s mandate is clear—safeguard patient information with unwavering resolve. It is a law that commands adherence to an exacting set of protocols, ensuring that the sanctity of patient information is preserved across every digital corridor and conversation.
- PCI DSS: In the realm of healthcare transactions, PCI DSS stands as the bulwark against financial data breaches. This suite of standards is the guardian of transactional integrity, ensuring that every credit card swipe and online payment is enveloped in layers of digital trust.
- HITRUST CSF: Tailored to the unique fabric of healthcare’s digital landscape, HITRUST CSF offers a versatile framework that adapts to the varied sizes and shapes of organizations within the sector. It provides a bespoke suit of armor, designed to defend against data breaches while maintaining the nimble movement required in the fast-paced world of healthcare.
DRIVING FORCES BEHIND THE CYBERSECURITY INDUSTRY
Advancement of connected healthcare technologies: The integration of IoMT devices has revolutionized patient care, but simultaneously, these connected technologies, including critical devices like pacemakers, have introduced new vulnerabilities, making them susceptible to cyberattacks that could have dire consequences for patient health and safety.
Escalating threats to sensitive data: An increase in medical identity theft, patent infringement disputes, and the loss of health records have catalyzed the healthcare sector’s demand for more sophisticated cybersecurity solutions, as hospitals and clinics face the continuous threat of having their data compromised.
Inherent risks in hospital infrastructure: The complexity of hospital technology systems, combined with the widespread use of mobile devices by medical staff, has heightened the risk profile of healthcare institutions, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals aiming to access a wealth of personal and financial patient data.
Pandemic-induced security challenges: The COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on healthcare cybersecurity has been significant, with the accelerated transition to digital healthcare platforms and databases revealing systemic vulnerabilities and sparking an increase in cyberattacks, thereby emphasizing the critical need for resilient cybersecurity defenses in a rapidly evolving threat environment.
Key Trends
The Impact of Connected Technology and IoMT
The integration of connected technology and IoMT devices in healthcare has significantly enhanced patient care but also increased cybersecurity risks. Devices such as pacemakers and other embedded medical devices, which use radio or network technology, can be vulnerable to attacks that could compromise patient health. The rise in patent infringement cases, medical identity fraud, and the loss of patient health records have further spurred the need for advanced cybersecurity solutions in the healthcare sector.
Cybersecurity Challenges in Hospitals
Hospitals are increasingly vulnerable to cyber-attacks due to their complex tech systems and reliance on mobile devices for staff communication and patient monitoring. Personal details collected by hospitals, including social security numbers and credit card information, make them prime targets for attackers. According to Cynerio’s 2022 State of Healthcare IoT Device Security report, over half of IoT devices in hospital settings contain critical cybersecurity vulnerabilities, with around one-third of bedside IoT healthcare devices posing significant cyber risks.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a notable impact on the healthcare cyber security market. The shift to digital healthcare platforms, clinical testing databases, and advanced healthcare devices during the pandemic led to an increase in cyberattacks. This trend highlighted the vulnerability of healthcare systems to cyber threats during times of crisis, driving the adoption of more robust cybersecurity services and solutions.
Healthcare Cybersecurity in India: A Critical Overview
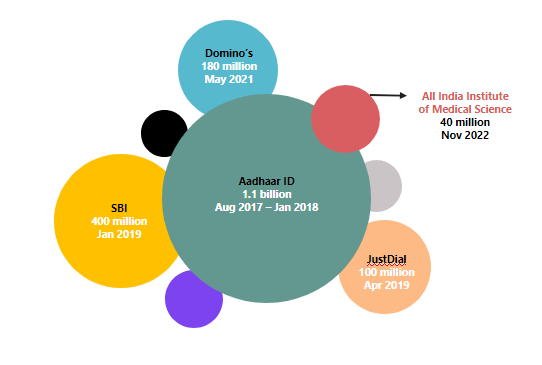
In India, the healthcare sector is increasingly becoming a hotspot for cybercriminals, with the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) reporting a dramatic 45% increase in cyberattack incidents following the year 2020. This alarming uptick underscores an urgent need for fortified cybersecurity protocols across healthcare institutions.
The landscape of cyber threats in Indian healthcare is diverse, ranging from ransomware that holds critical data hostage to phishing scams that trick healthcare workers into divulging sensitive information. In 2021, a significant breach occurred when a renowned Mumbai hospital fell victim to a ransomware attack. This not only resulted in the encryption and potential loss of vital patient data but also caused considerable disruption to the hospital’s daily operations, underscoring the tangible impact of cyber threats on patient care and institutional integrity.
Statistically, the sector has seen a concerning rise in the frequency and sophistication of attacks. As per a study by Seqrite, the enterprise arm of Quick Heal Technologies, over 7 million data records of Indian healthcare were compromised in just the first half of 2021. These breaches not only have immediate operational impacts but also carry long-term reputational and financial repercussions.
To combat these issues, Indian healthcare organizations are mandated to comply with the Information Technology (IT) Act, which outlines provisions for data protection and security, which are poised to be further strengthened by the proposed Personal Data Protection Bill. These regulations set the groundwork for data privacy and security, requiring healthcare entities to implement stringent cybersecurity measures.
Moreover, real-world examples, such as the ransomware attack on the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) in 2019, which led to the theft of personal information and hampered patient care, provide a stark reminder of the criticality of cybersecurity readiness. This incident, among others, highlights the necessity for continuous investment in cybersecurity infrastructure and the adoption of best practices to safeguard against the evolving spectrum of cyber threats.
In conclusion, the state of cybersecurity in Indian healthcare is at a decisive point, requiring immediate and sustained action. Organizations must prioritize the establishment of robust cybersecurity frameworks, engage in thorough risk assessments, and ensure compliance with national regulations to protect against the ever-growing threat landscape.
Balancing Cybersecurity Products and Services
Choosing between cybersecurity products and services should be based on an organization’s specific needs. Large healthcare networks with complex IT infrastructures may benefit from comprehensive solutions like advanced endpoint protection and firewalls, supported by a dedicated SOC. In contrast, smaller clinics with limited IT resources might find greater value in cloud-based cybersecurity services.
Conclusion:
A Strategic Approach to Cybersecurity in Healthcare
For healthcare CXOs, developing a proactive and strategic approach to cybersecurity is imperative. This involves not only investing in the latest security technologies but also cultivating a culture of security awareness throughout the organization. A nuanced understanding of both global and local regulatory standards is also crucial. By adopting these strategies, healthcare leaders can safeguard their data and maintain the trust and safety of their patients.
For further clarifications or support, please write to ask@paradigmit.com

